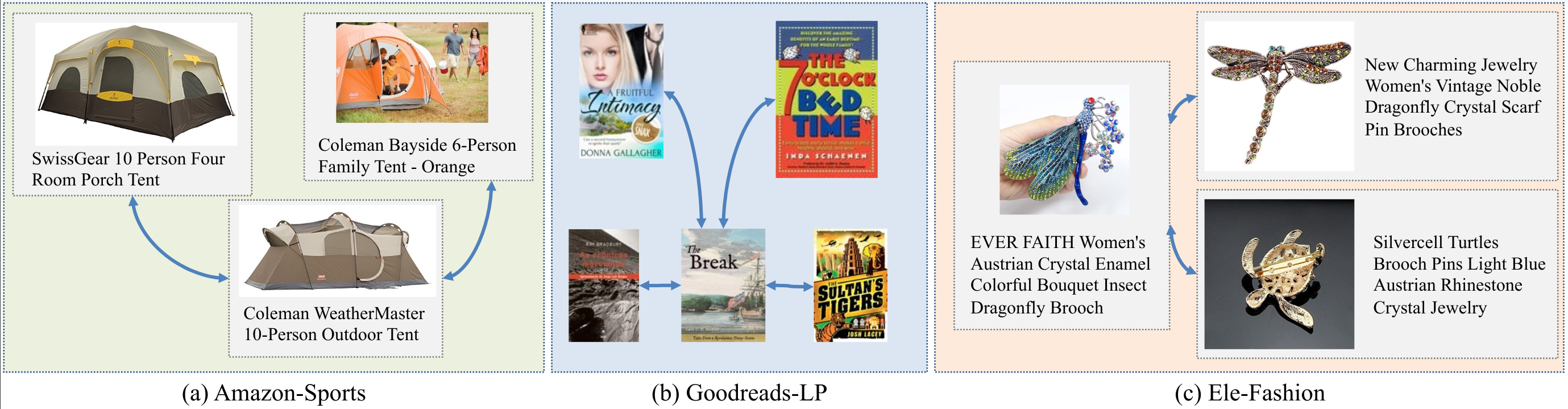
Associating unstructured data with structured information is crucial for real-world tasks that require relevance search. However, existing graph learning benchmarks often overlook the rich semantic information inherent in each node. To bridge such gap, we introduce the Multimodal Graph Benchmark (MM-Graph), the first comprehensive multi-modal graph benchmark that incorporates both textual and visual information. MM-Graph surpasses previous efforts, which have primarily focused on text-attributed graphs with various connectivity patterns.
MM-Graph consists of five graph learning datasets of various scales and tasks. These datasets feature multimodal node features, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation of graph learning algorithms in real-world scenarios. To facilitate research on multimodal graph learning, we further provide an extensive study on the performance of various graph neural networks in the presence of features from various modalities. MM-Graph aims to foster research on multimodal graph learning and drive the development of more advanced and robust graph learning algorithms. By providing a diverse set of datasets and benchmarks, MM-Graph enables researchers to evaluate and compare their models in realistic settings, ultimately leading to improved performance on real-world applications that rely on relevance search in multimodal graph data.